
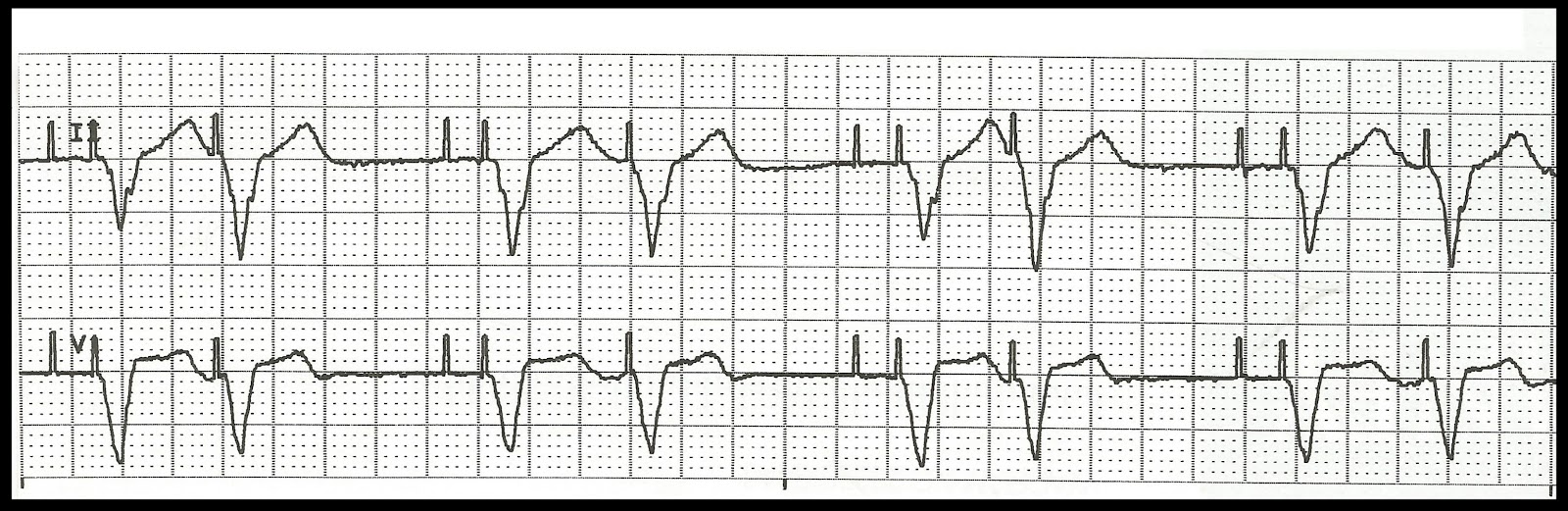
Atrial capture may not be discernible because of the short AV interval (e.g., V leads 4-6 in this ECG), so perusal of all 12 leads is mandatory. The short AV interval is designed to disallow fusion QRS complexes by usurping native AV conduction, thus confirming ventricular capture. The rate of 100 bpm (magnet rate) is nonprogrammable, as is the short AV interval.

(A) This 12-lead ECG illustrates DOO function in use by several manufacturers. Because magnet placement eliminates sensing, pacing output occurs despite the existence of a spontaneous cardiac rhythm repetitive atrial or ventricular beating is only very rarely a clinical consequence. 7.5A ) other manufacturers set a rapid magnet rate for a specific number of cycles, followed by a slower rate (see Fig. It varies with the manufacturer several manufacturers set a constant magnet rate well above the expected spontaneous rate (e.g., 100 beats per minute) in order to allow myocardial depolarization (pacing) to be confirmed ( Fig. The magnet rate (designated AOO, VOO, or DOO, as sensing, and therefore response to a sensed signal, do not occur thus, the letter “O”-an asynchronous mode) is that nonprogrammable rate that occurs when a magnet is placed over the pulse generator. Whereas these rates are often programmed to be the same, the sensor-based rate can be programmed to exceed the tracking rate in response to exercise, thereby avoiding rapid ventricular paced rates triggered by supraventricular tachycardias. The maximum tracking rate is that rate at which ventricular pacing will be triggered by native P waves in a 1:1 relationship (atrial based) the maximum sensor-based rate is the highest programmed rate dictated by sensor input to the pulse generator. The upper rate limit, which is either atrial (native P wave) based or sensor based, is the programmed maximum pacing rate that can occur. In devices programmed to rate responsiveness, the base rate is the lowest programmed rate at rest. The base rate (lower rate limit, standby rate) of a pacing system is that programmed rate at which pacing will occur if there is no spontaneous cardiac depolarization. This represents a dual-chamber pacemaker with ventricular pacing in response to atrial sensing (P-synchronous pacing). This 12-lead ECG tracing with rhythm strips shows a ventricular paced rhythm, but each ventricular paced beat is preceded by a sinus P wave (sinus rate of 55 bpm).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
